我們使用javax.imageio.ImageIO類別的read方法,獲得回傳BufferedImage Object.
代表此物件已經載入記憶體緩衝區的影像檔。
接下來我們用三個方法來取得相關的影像資訊:
public void getReadWriteFormat(){
String[] readSuffixes = ImageIO.getReaderFileSuffixes(); //讀取檔案格式副檔名
String[] writeSuffixes = ImageIO.getWriterFileSuffixes(); //寫入檔案格式副檔名
String canReadFormat = "";
String canWriteFormat = "";
for(int i=0 ; i<readSuffixes.length ; i++)
canReadFormat += readSuffixes[i]+",";
for(int i=0 ; i< writeSuffixes.length ; i++)
canWriteFormat += writeSuffixes[i]+",";
//去除最後一個逗點
canReadFormat = canReadFormat.substring(0, canReadFormat.length()-1);
canWriteFormat = canWriteFormat.substring(0, canWriteFormat.length()-1);
System.out.println("JDK支援對"+ canReadFormat +"格式讀取");
System.out.println("JDK支援對"+ canWriteFormat +"格式寫入");
}
private String getColorSpaceName(int type) {
String name = ""; //先設定字串空白,方便接下來使用
switch(type){
case 0:
name = "TYPE_XYZ";
break;
case 1:
name = "TYPE_Lab";
break;
case 2:
name = "TYPE_Luv";
break;
case 3:
name = "TYPE_YCbCr";
break;
case 4:
name = "TYPE_Yxy";
break;
case 5:
name = "TYPE_RGB";
break;
case 6:
name = "TYPE_GRAY";
break;
case 7:
name = "TYPE_HSV";
break;
case 8:
name = "TYPE_HLS";
break;
case 9:
name = "TYPE_CMYK";
break;
case 11:
name = "TYPE_CMY";
break;
}
return name;
}
下圖為 Plan views of RGB gamut in (A) YUV, (B) YIQ and (C) YCbCR colour spaces. In YCbCr the screen primaries are evenly spaced, as in the RGB-CMY hue circle, though in the reverse order.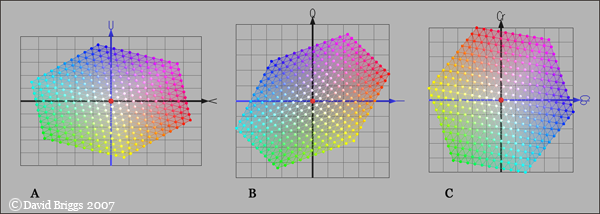
private String getTransparencyName(int type){
String name = "";
switch(type){
case 1:
name = "OPAQUE, 完全不透明, 所有像素的Alpha值都為1.0";
break;
case 2:
name = "BITMASK, 完全不透明(Alpha值都為1.0) or 完全透明(Alpha值都為0.0)";
break;
case 3:
name = "TRANSLUCENT, Alpha值為0.0~1.0 (含兩者)";
break;
}
return name;
}
參考資料:深智數位《CV+AI自己動手完成圖像搜尋引擎》
The Dimensions of Colour, CIE LAB, CIE LUV YCbCr
Value-by-alpha maps | Andy Woodruff
